Siachen Glacier: The Frozen Frontier and Environmental Battleground
Nestled in the Karakoram Range of the Himalayas, the Siachen Glacier stands as one of the world's highest and most inhospitable battlefields.
Beyond its military significance, this formidable glacier holds ecological importance as a vast reservoir of freshwater.
In this blog post, we will venture into the captivating realm of the Siachen Glacier, exploring its unique characteristics, geopolitical significance, and the environmental challenges it faces.
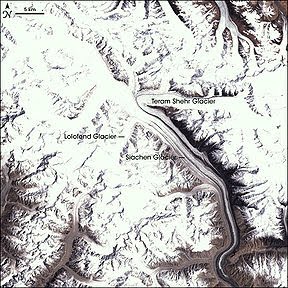 Location and Characteristics: The Siachen Glacier is located in the disputed region of Kashmir, between India and Pakistan. Spanning approximately 76 kilometers in length, it is the world's longest non-polar glacier. The glacier is characterized by its rugged terrain, extreme cold temperatures, and colossal ice formations.
Location and Characteristics: The Siachen Glacier is located in the disputed region of Kashmir, between India and Pakistan. Spanning approximately 76 kilometers in length, it is the world's longest non-polar glacier. The glacier is characterized by its rugged terrain, extreme cold temperatures, and colossal ice formations.Geopolitical Significance: The Siachen Glacier has been a contentious area between India and Pakistan since 1984, with both nations maintaining military presence due to border disputes. The hostile conditions of the glacier, coupled with the geopolitical tensions, have made it one of the world's highest battlegrounds.
Environmental Importance: Beyond its militarized status, the Siachen Glacier holds immense ecological significance. It serves as a crucial source of freshwater for several major rivers in the region, including the Indus River. The glacier's meltwater sustains the livelihoods of millions of people downstream, supporting agriculture, hydropower generation, and ecosystems.
Environmental Challenges: The Siachen Glacier faces significant environmental challenges, compounded by military activities and climate change:
a. Ecological Footprint: Military operations in the region have left a substantial ecological footprint, including waste, pollution, and the use of non-biodegradable materials. These activities disrupt the fragile mountain ecosystem and threaten local biodiversity.
b. Melting and Glacial Retreat: The Siachen Glacier, like many glaciers worldwide, is experiencing the effects of climate change. Rising temperatures have led to accelerated melting and retreat of the glacier. This has implications for water availability, downstream ecosystems, and the stability of glacial lakes.
c. Natural Hazards: The extreme climate and rugged terrain of the Siachen Glacier pose risks of avalanches, crevasses, and icefalls. These hazards not only endanger military personnel but also complicate rescue and relief operations in case of emergencies.
Peace Initiatives and Environmental Cooperation: Efforts have been made to transform the Siachen Glacier region into a "Peace Park," highlighting the importance of environmental conservation and peaceful coexistence. Collaborative environmental projects between India and Pakistan, such as glaciological research and data sharing, aim to mitigate environmental challenges and promote cooperation.
Conservation and Sustainable Practices: Conservation measures are being implemented to address the environmental impact on the Siachen Glacier. Waste management practices, eco-friendly protocols, and awareness campaigns are being pursued to minimize the ecological footprint in the region. Additionally, scientific research and monitoring are crucial for understanding the glacier's behavior and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies.
The Siachen Glacier represents a unique intersection of geopolitics, environmental significance, and human endeavor. While it remains a heavily militarized zone, the environmental challenges it faces cannot be ignored. By fostering environmental cooperation, adopting sustainable practices, and addressing the impacts of climate change, we can work towards preserving the ecological integrity of the Siachen Glacier. Ultimately, prioritizing the conservation of this frozen frontier is vital to ensure the availability of freshwater resources and protect the fragile mountain ecosystems that depend on it.
Visit Official Home Page




0 Comments